Keto What Is It?
A keto diet is well known for being a low carb diet, where the body produces ketones in the liver to be used as energy. It’s referred to as many different names – ketogenic diet, low carb diet, low carb high fat (LCHF), etc.
When you eat something high in carbs, your body will produce glucose and insulin.
- Glucose is the easiest molecule for your body to convert and use as energy so that it will be chosen over any other energy source.
- Insulin is produced to process the glucose in your bloodstream by taking it around the body.
Since the glucose is being used as a primary energy, your fats are not needed and are therefore stored. Typically on a normal, higher carbohydrate diet, the body will use glucose as the main form of energy. By lowering the intake of carbs, the body is induced into a state known as ketosis.
Ketosis is a natural process the body initiates to help us survive when food intake is low. During this state, we produce ketones, which are produced from the breakdown of fats in the liver.
The end goal of a properly maintained keto diet is to force your body into this metabolic state. We don’t do this through starvation of calories but starvation of carbohydrates.
Our bodies are incredibly adaptive to what you put into it – when you overload it with fats and take away carbohydrates, it will begin to burn ketones as the primary energy source. Optimal ketone levels offer many health, weight loss, physical and mental performance benefits.
What Do I Eat on a Keto Diet?
To start a keto diet, you will want to plan ahead. That means having a viable diet plan ready and waiting. What you eat depends on how fast you want to get into a ketogenic state (ketosis). The more restrictive you are on your carbohydrates (less than 25g net carbs per day), the faster you will enter ketosis.
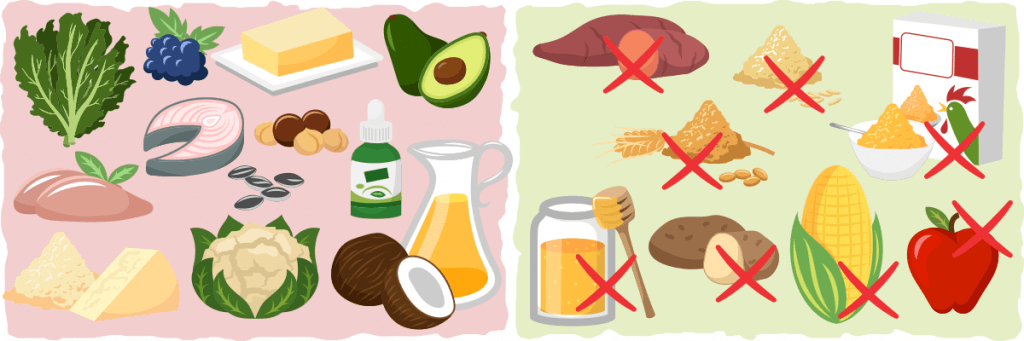
You want to keep your carbohydrates limited, coming mostly from vegetables, nuts, and dairy. Don’t eat any refined carbohydrates such as wheat (bread, pasta, cereals), starch (potatoes, beans, legumes) or fruit. The small exceptions to this are avocado, star fruit, and berries which can be consumed in moderation.
Do Not Eat
- Grains – wheat, corn, rice, cereal, etc.
- Sugar – honey, agave, maple syrup, etc.
- Fruit – apples, bananas, oranges, etc.
- Tubers – potato, yams, etc.
Do Eat
- Meats – fish, beef, lamb, poultry, eggs, etc.
- Leafy Greens – spinach, kale, etc.
- Above ground vegetables – broccoli, cauliflower, etc.
- High Fat Dairy – hard cheeses, high fat cream, butter, etc.
- Nuts and seeds – macadamias, walnuts, sunflower seeds, etc.
- Avocado and berries – raspberries, blackberries, and other low glycemic impact berries
- Sweeteners – stevia, erythritol, monk fruit, and other low-carb sweeteners
- Other fats – coconut oil, high-fat salad dressing, saturated fats, etc.
Try to remember that keto is high in fat, moderate in protein, and very low in carbs. Your nutrient intake should be something around 70% fats, 25% protein, and 5% carbohydrate.
Typically, anywhere between 20-30g of net carbs is recommended for everyday dieting – but the lower you keep your carbohydrate intake and glucose levels, the better the overall results will be. If you’re doing keto for weight loss, it’s a good idea to keep track of both your total carbs and net carbs.
Protein should always be consumed as needed with fat filling in the remainder of the calories in your day.
You might be asking, “What’s a net carb?” It’s simple really! The net carbs are your total dietary carbohydrates, minus the total fiber. I recommend keeping total carbs below 35g and net carbs below 25g (ideally, below 20g).







